It holds the cheek to the teeth and assists with chewing. Due to its function of puffing out cheeks it is also called trumpeter muscle.

Buccinator Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Exercise
Couper and Myot coined the term buccinator in the year 1694.

What is the buccinator muscle called. The buccinator muscle is divided into three parts. Action Retracts angle of mandibula compresses cheek. Buccinator also prevents cheeks from inverting in between the occlusal surfaces of the teeth and being bitten.
What passes through the Buccinator muscle. The buccinator muscle is served by the buccal branch of cranial nerve VII also known as the facial nerve. The buccinator muscle plays an active role along with orbicularis oris and superior constrictor muscle during swallowing mastication blowing and sucking.
Couper and Myot coined the term buccinator in the year 16942 This muscle is sometimes referred to as an accessory muscle of mastication due to its role in compressing the cheeks inwards against molars thus aiding in chewing and swallowing3 Due to its function of puffing out cheeks it is also called trumpeter muscle. The muscles of the face are between the skin and the bones of the face or skull. In human anatomy the orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth.
What is this muscle called. Anterior posterior and superior auricular muscles. This is why the buccinator muscle is also called the trumpet muscle.
The major head flexors are the sternocleidomastoid muscles with the help of the muscles attached to the hyoid bone. Other muscles playing supporting roles to help you eat and drink are the buccinator and the mylohyoid. The buccinator muscle is a facial muscle located in the cheeks.
A buccinator B zygomaticus C platysma D masseter A buccinator 2 Spasms of this straplike muscle often result in wryneck or torticollis. This compression of the cheek serves several different. Nerve Buccal branch of facial.
In total there are. They are not surrounded by a fascia with the exception of the buccinator. The subcutaneous cheek tissue contains many muscle fibers that participate in forming the cheeks.
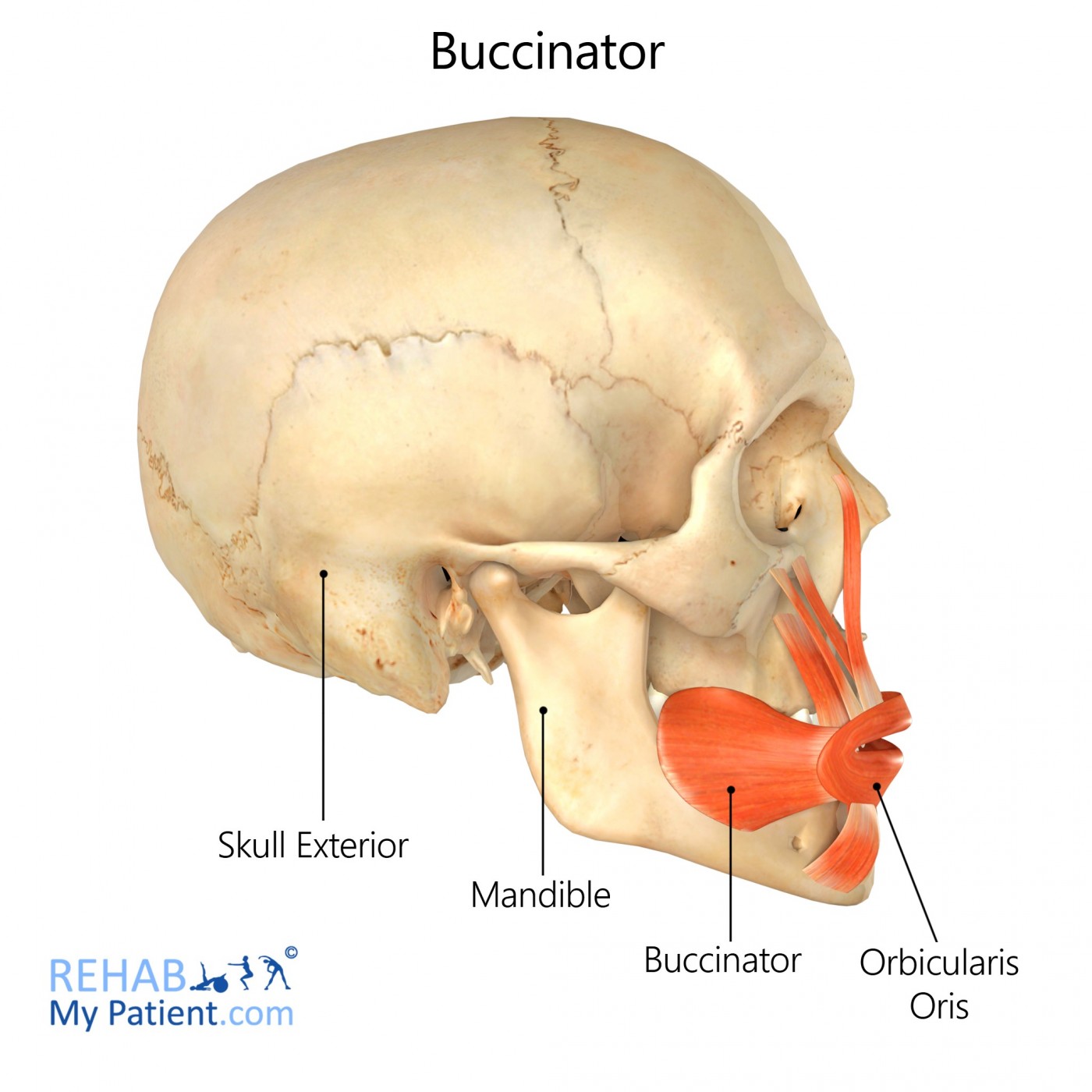
The fascia is a membrane that allows free movement without friction. A muscle of the cheek. The buccinator muscle is the major facial muscle underlying the cheek.
This muscle is sometimes referred to as an accessory muscle of mastication due to its role in compressing the cheeks inwards against molars thus aiding in chewing and swallowing. The sternocleidomastoid muscle inserts on the Mastoid process and lateral portion of nuchal line In general a muscle that crosses on the anterior side of a joint produces flexion Muscles of the hamstrings group biceps femoris semitendinosus semimembranosus Describes the orbicularis oris control mouth and lips Which muscle group is involved when a pulled groin occurs thigh adductors What. The buccinator muscle is served by the buccal branch of cranial nerve VII also known as the facial nerve.
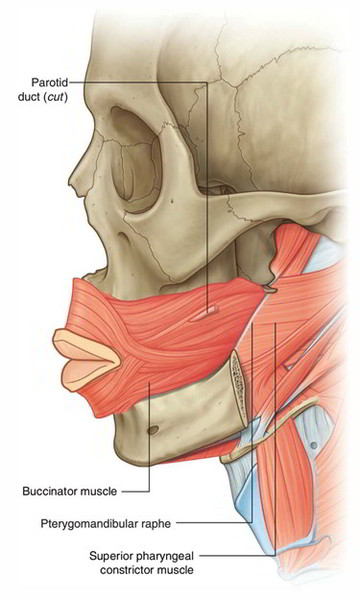
Two small branches form the posterosuperior alveolar artery which is a branch of internal maxillary artery enter the buccinator muscle posterosuperiorly and supply the surrounding area. The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and mandible. Insertion Orbicularis oris at angle of jaw.
What is Buccinator muscle. The buccinator also buccinator muscle latin. Depressor septi nasalis and procerus muscles.
The masseter muscle is. Until recently it was misinterpreted as a sphincter or circular muscle but it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity. Origin Buccinator ridge of mandible alveolar process of maxilla pterygomandibular ligament.
Buccinator depressor anguli oris depressor labii inferioris levator anguli oris levator labii superioris mentalis orbicularis. The main action of this muscle is to compress the cheek against the teeth. The buccinator muscle is a facial muscle that is a part of a group of muscles known as the buccolabial group.
The buccinator muscle has another interesting function and that is expelling the air from the inflated vestibule while playing a wind instrument such as the trumpet. Muscles connecting to the hyoid bone are important for swallowing and speech. This is why the buccinator muscle is also called the trumpet.
The four main mastication muscles masseter medial pterygoid lateral pterygoid and temporalis are attached to the skull and the lower jaw. Buccinator also prevents cheeks from inverting in between the occlusal surfaces of the teeth and being bitten. Musculus buccinator is a facial muscle that participates in forming the anterior part of the cheek and the lateral wall of the oral vestibule.
The buccinator muscle has another interesting function and that is expelling the air from the inflated vestibule while playing a wind instrument such as the trumpet. Most are flat beams. A facial muscle that arises from the nasal bone and a cartilage in the side of the nose and that inserts into the skin of the forehead between the eyebrows.
A nursing infant develops a powerful sucking muscle that adults also use for whistling. The buccinator muscle is the primary muscle involved in cheek compression. The buccinator muscle is served by the buccal branch of cranial nerve VII also known as the facial nerve.
These muscles are responsible for the movement of the jaw joint. The biggest cheek muscles are the masseter and the buccinator. In order to propel food down to the esophagus the pharyngeal constrictor muscles are used.
The buccinator muscle is the major facial.

The Muscles Of The Head And Neck Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/buccinator-muscle-3/VuJL5stbW51J5sc1aSv6w_Buccinator_M._01.png)
Buccinator Origin Insertion Innervation Function Kenhub

Buccinator Muscle Definition Nerve Study Com