The platysma muscle is controlled by the cranial nerve VII which. Buccinator is pronounced booksinator the oos as in goose.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/rami-buccales-nervi-facialis-2/hrIRNBHUXAO40Lfwdk9Rg_Rr._buccales_01.png)
Buccinator Origin Insertion Innervation Function Kenhub
The buccinator muscle is the major facial muscle underlying the cheek.

What is the buccinator muscle connected to. The facial muscles are striated muscles that link the skin of the face to the bone of the skull to perform important functions for daily life including mastication and expression of emotion. Raphe is from the Greek rhaphé meaning seam or suture suture referring to a joining. So it also comes in when we talk laugh or yell.
It holds the cheek to the teeth and assists with chewing. It forms the anterior part of. Participates in the chewing process and is responsible for opening the mouth.
The buccinator is externally surrounded by the buccopharyngeal fascia and both the buccinator muscle and the buccopharyngeal fascia lie underneath the buccal fat pad Woodburne and Burkel 1994. It forms the anterior part of the. And it contributes to the action of chewing.
While the individual movements these muscles produce are varied and diverse. Buccinator cheek muscle The Buccinator is one of the largest facial muscles and sits right on the inside of the cheek next to the teeth. Oral Head and Neck Oncology and Reconstructive Surgery 2018.
Buccinator is flat located within the cheek and spread parallel to the great axis of the mouth of which it closes the cavity laterally. A to initiate abduction of the arm to stabilize the shoulder joint and to help prevent downward dislocation of the humerus. It is a large muscle extending from the eyebrows to the occipital bone.
It presses the cheek against the teeth which helps keep food between our teeth for chewing. Pulls the corners of the mouth back and compresses the cheek What muscle of the mouth is also known as an accessory muscle of mastication and why. There are several small facial muscles one of which is the.
What is the action of the buccinator muscle. C to extend and medially rotate the humerus and to act as a synergist of the latissimus dorsi. In the neck this muscle covers the sternocleidomastoid which is a deep muscle that runs up vertically on each side of the neck.
THE LEVATOR ANGULI ORIS MUSCLE. The human face possesses over two dozen individual muscles on each side - upwards of 30 depending on how they are counted. The buccinator mechanism was investigated by injecting alginate into the buccal space of volunteers and.
Compressing the cheek. It is an assistant muscle of mastication chewing and in neonates it is used to suckle. This muscle contributes to the naso-labial fold in the cheek.
Buccinator is from the Latin buccinare meaning to blow a trumpet. This structure is called the modiolus it is located at the angles of the mouth and it is primarily formed by the buccinator orbicularis oris risorius depressor anguli oris and zygomaticus major muscles. And finally the occipitofrontal.
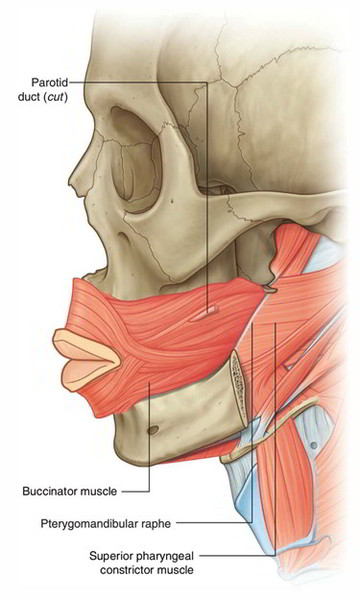
The part located between the masseter and the orbicular muscle of the mouth constitutes the anatomical base of. The buccinator ˈbksnetr is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. Prevents you from biting your cheek as you eat.
The majority of the face is composed of the buccinator muscle which compresses the cheek. This muscle is located in the upper part of the lower jaw. The buccinator muscle is a muscle that is located in each of the cheeks of the face.
The buccinator muscle is served by the buccal branch of cranial. The buccinator muscle helps with these functions two of which go beyond eating. The buccinator muscle is a thin quadrilateral facial muscle that is the main component of the cheek It belongs to the buccolabial group of facial muscles along with levator labii superioris alaeque nasi levator labii superioris zygomaticus major zygomaticus minor levator anguli oris risorius depressor labii inferioris mentalis orbicularis oris incisivus superior and inferior muscles.
The buccinator muscle M. Controls airflow through the mouth to whistle and suck inblow out air essential for meditative breathing and playing some musical instruments. B to help hold the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity and rotate the humerus laterally.
This muscle allows you to whistle blow and suck. The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. This muscle receives electrical impulses from the brain through the cranial nerve VII and it receives its.
The majority of the mouth muscles are connected by a fibromuscular hub onto which their fibers insert. The buccinator muscle is a significant landmark for lesions of the buccal mucosa in that 60 of superficial cancers that do not clinically appear to involve the muscle actually do have muscle involvement30. Orbicularis oris muscle also known as musculus orbicularis oris is a complex multi-layered muscle which attaches through a thin superficial musculoaponeurotic system to the dermis of the upper lip and lower lip and serves as an attachment site for many other facial muscles around the oral region1 This muscle may be regarded as a single muscle anatomically but functionally it appears to.
However the connecting fascia between the buccinator and the tendons of the temporalis is located superficial to the buccal fat pad.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-masseter/jgE3c73f9mnWIUUlafELQ_Masseter_muscle_01.png)
Masseter Muscle Anatomy Origin Insertion Function Kenhub
Blooming In Adelaide Breastfed Baby And The Bucinnator Muscle Did You Know The Buccinator Muscle Is One Of The First Muscles That A Baby Can Control The Sucking Reflex Of A
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/buccinator-muscle-3/VuJL5stbW51J5sc1aSv6w_Buccinator_M._01.png)
Buccinator Origin Insertion Innervation Function Kenhub
3d4medical From Elsevier Which Nerve Provides Motor Innervation To The Buccinator Muscle A Auriculotemporal Nerve B Buccal Branches Of Vii C Buccal Nerve D Marginal Mandibular Nerve Comment Your Answer Below